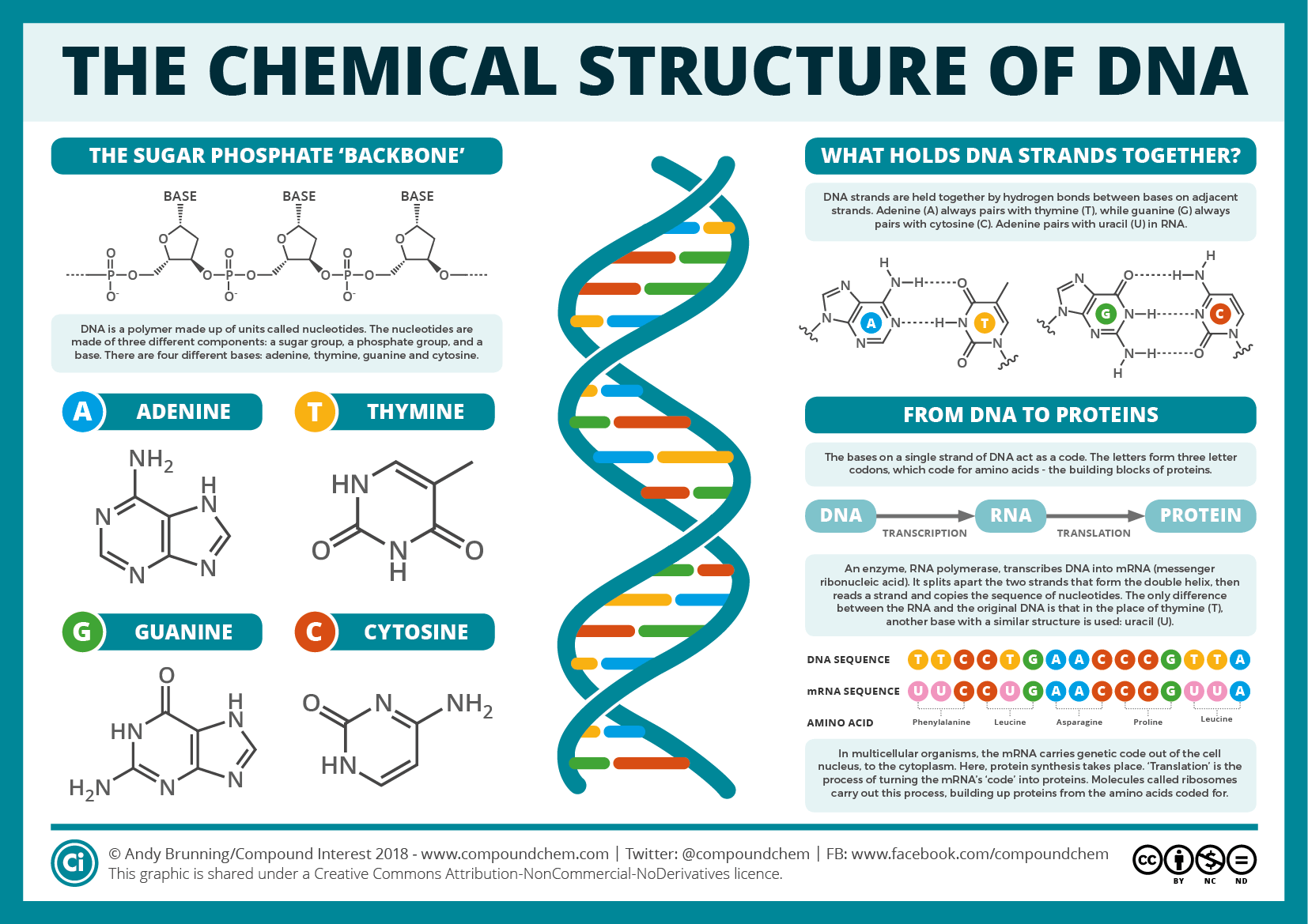
Oct 07, 19 · DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid is a type of molecule known as a nucleic acid It consists of a 5carbon deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base Doublestranded DNA consists of two spiral nucleic acid chains that are twisted into a double helix shape This twisting allows DNA to be more compactThis mitochondrial DNA is more like bacterial DNA—a single long, circular piece of DNA made up of two strands of DNA A DNA strand is a long, thin molecule—averaging only about two nanometers (or two billionths of a meter) in width That isWhen the DNA molecule is inactive, the bases are linked by these hydrogen bonds and the molecule is in its spiralshaped state When DNA is being used—either being copied (a process called replication) or being employed to build proteins (involving the processes of transcription and translation)—the DNA molecule must be opened up, essentially "unzipped" between the bases

Single Stranded Dna Vs Double Stranded Dna Quick Differences In 5 Min Youtube
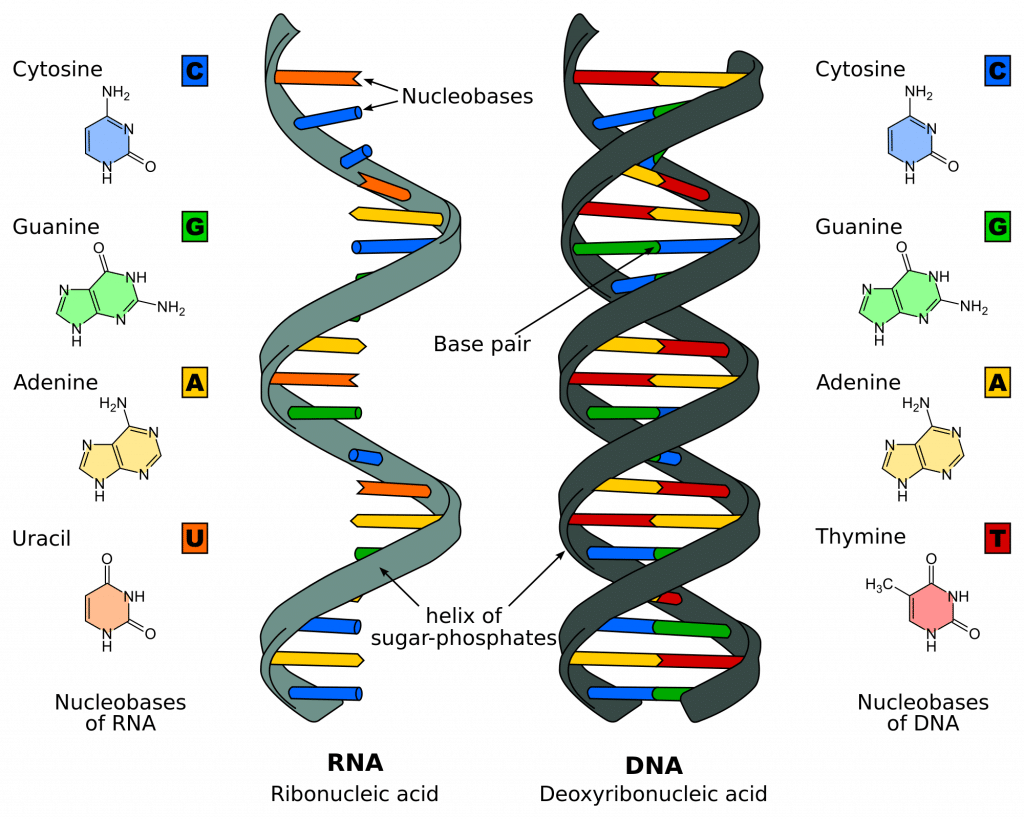
Simplified double stranded dna molecule
Simplified double stranded dna molecule-Apr 24, 10 · To do this, it first has to unzip the nitrogenous bases All the pairs of "AT" and "GC" are separated The DNA then has two single strands At this point new pairs are made, along with a new phosphate backbone, to create two new copies of DNA Each single strand then pairs with a correct complementary base to create a new doublestranded pieceThe DNA double helix is a description of the molecular shape of a doublestranded DNA molecule It explains how DNA is copied when a cell divides, how it is passed down to generations, and more Learn more at Ancestry!


The Abc Of Genomics Advanced Nutrigenomics Llc
Which part of the DNA molecule contributes to the property?May 27, 17 · A phosphodiester linkage essentially has a phosphate molecule forming two covalent bonds and a series of these bonds creates the two spines of a doublestranded DNA molecule Alternating sugar and phosphate residues results in one end of every DNA strand having a free phosphate group attached to the fifth carbon of a deoxyribose sugarAnswer For a given gene, only one strand of DNA is transcribed This strand (called the template) will be complementary to the RNA and also to the other strand (called the nontemplate or coding strand) Consequently, the nucleotide sequence of the RNA must be the same as that of the nontemplate strand of the DNA (except that the Ts are instead
Extensive manipulations involved in the preparation of DNA samples for sequencing have hitherto made it impossible to determine the precise structure of doublestranded DNA fragments being sequenced, such as the presence of blunt ends, singlestranded overhangs, or singlestrand breaks We here descNov 12, 18 · "This is the first bifacial molecule that can invade doublestranded DNA or RNA under biologically relevant conditions" DNA, which contains all of an organism's genetic information, is made up of1 Draw the chemical structure of the following doublestranded DNA molecule Then, identify and label the bonds that exist in the DNA molecule you have drawn 5' ATTG IIII TAAC 5 ii What is the net charge of the DNA molecule?
Oct 01, 15 · This was followed by evidence for double stranded RNA by Weismann and August in 1968 Reverse transcription is the process of making a double stranded DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecule from a single stranded RNA (ribonucleic acid) template It is called reverse transcription as it acts in the opposite or reverse direction to transcriptionSubscribe Nowhttp//wwwyoutubecom/subscription_center?add_user=ehoweducationWatch Morehttp//wwwyoutubecom/ehoweducationDNA is two different strands of6 Why is the order of the bases important?



4 A Simplified Double Stranded Structure Of Dna Download Scientific Diagram
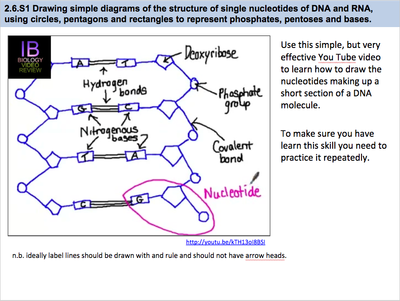


2 6 Dna Rna Structure
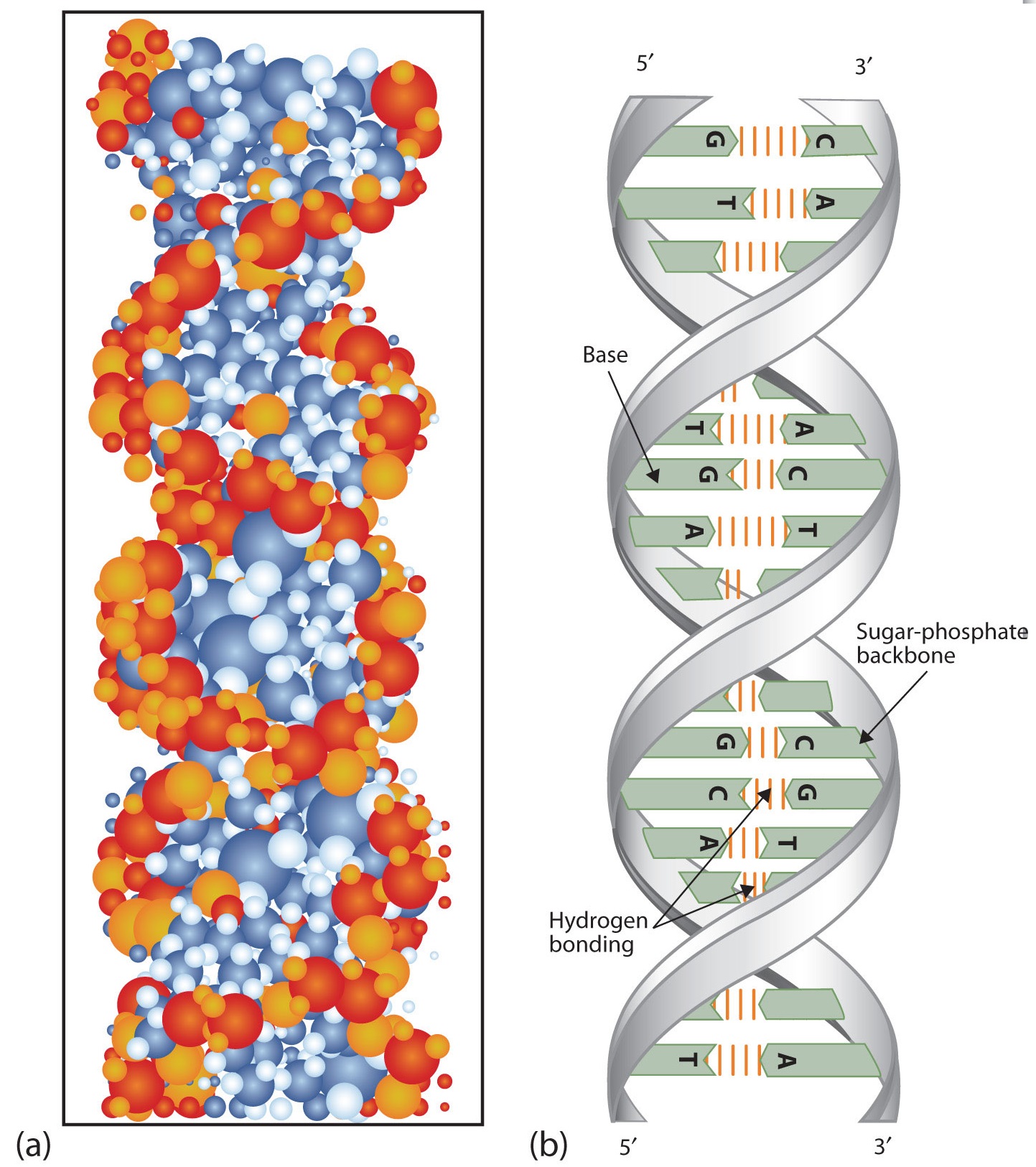
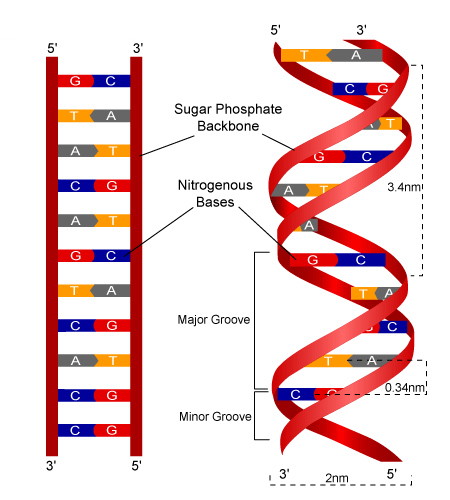
Jun 16, 17 · Structure of DNA It is made of two polynucleotide chains Sugar and phosphate form the backbone of the DNA molecule and the bases project inside DNA is double stranded, righthanded coiled;Mar 06, 21 · DNA is a doublestranded molecule made up of complementary, antiparallel strands Based on what you know about complementary base pairing, fill in the rest of the details in the figure *The nucleotide pairs in doublestranded DNA follow the basepairing rules A with T, and G with C The complementary strands are antiparallel, with one strandThe strands of DNA run antiparallel, or in opposite directions the 5' end of one strand is paired with the 3' end of the other This is illustrated in the figure below This structure places the nonpolar bases of DNA in the center of the doublestranded molecule, surrounded by the charged phosphate groups This has two functional



Concepts And Terms In Genetic Research A Primer


The Structure Of Dna
7 Explain the base pair rules 8 If one strand of DNA has a sequence of 5' ATG CAG TCT GAT CAT 3', what would its complementary strand be?A DNA strand is simply a string of nucleotides joined together I can show how this happens perfectly well by going back to a simpler diagram and not worrying about the structure of the bases The phosphate group on one nucleotide links to the 3' carbon atom on the sugar of another one In the process, a molecule of water is lost another condensation reactionIii The human genome is distributed in 23 pairs of



Diagrams Of Molecular Structure Amine Bases Hydrogen Bonding Base Pairing In Dna And Rna Thymine Adenine Cytosine Guanine Uracil Hydrogen Bonds Hold Hexix Together Double Strabded Rna Dna Organic Nitrogen Compounds Organonitrogen


The Structure Of Dna
May 14, 15 · Glossary deoxyribose a fivecarbon sugar molecule with a hydrogen atom rather than a hydroxyl group in the 2′ position;Agrobacterium tumefaciensmediated genetic transformation involves transfer of a singlestranded TDNA molecule (T strand) into the host cell, followed by its integration into the plant genome The molecular mechanism of TDNA integration, the culmination point of the entire transformation process, remains largely obscureSubmicrometer elasticity of doublestranded DNA (dsDNA) governs nanoscale bending of DNA segments and their interactions with proteins Singlemolecule force spectroscopy, including magnetic tweezers (MTs), is an important tool for studying DNA mechanics However, its application to short DNAs under 1 μm is limited We developed an MTbased method for precise


Structure Of Dna And Rna



Nucleic Acids Dna And Rna Primer Of Genetic Analysis A Problems Approach 3rd Ed
Aug 06, 19 · Here, we investigate the overstretching transition of four different NA duplexes by singlemolecule force measurements These duplexes are doublestranded DNA (dsDNA), dsRNA, a heteroduplex with the DNA strand under tension (RNADNA), and a heteroduplex with the RNA strand under tension (DNARNA), respectivelyCytosine pairs with guanine so wherever cytosine appears on one half of the DNA molecule, guanine will be on the other half and vice versa 7 In this chapter, DNA sequencing was discussed in relation to hereditary spastic paraplegia Find out how DNA sequencing is being used with other diseases such as sicklecell anaemiaDNA is a double stranded helix that carries the instructions for building and maintaining an organism DNA is made up of A phosphate backbone A pentose sugar, deoxyribose One of four organic bases adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine DNA is a ~ molecule made of four subunits called nucleotides


3 3 Dna Structure Bioninja
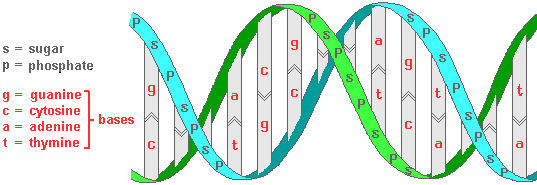


Biological Basis Of Heredity Molecular Level Of Genetics
The two chains are antiparallel, they are opposite in direction One chain is in 5 ′ →3 ′ direction, the other is in 3 ′ →5′ direction This39Outline the structure of part of a double stranded DNA molecule with the help of a simplified diagram (5 marks) Topic 72 MCQ 1 Refer to the diagram below showing the posttranscription changes happening in RNAThe ladder model of DNA is a simplified representation of the actual structure and shape of a DNA molecule In reality, the strands of DNA form a double helix Refer to the double helix diagram in Model 1 and describe its shape using a complete sentence The Helix are ovals


The Structure Of Dna



Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks
5 What 3 structures make up a nucleotide?Dec 05, 13 · The estimated value of its bending persistence length as large as ≈ 50 nm implies the doublestranded (ds) DNA barely bends over the length shorter than that Recently, however, there have been a series of experimental evidences that, on such short length scales, sharp bendings occur much more readily than predicted by the WLC model 6, 7 Experiments have shown that under strong tension the Bform DNA9 If a double stranded molecule of DNA was found to be %



Dna Synthesis Wikipedia



Dna Structure Simplified Biology
Aug 24, · When a cell prepares to divide, the DNA helix splits down the middle and becomes two single strands These single strands serve as templates for building two new, doublestranded DNA molecules each a replica of the original DNA molecule In this process, an A base is added wherever there is a T, a C where there is a G, and so on until all ofThe freefloating nucleotides that are available in the nucleus are then paired up one after the other onto the exposed bases of the DNA strand The end result is two DNA molecules, each composed of one strand of the old DNA molecule and a newly assembled strand 1 13Jun 04, · (A) Experimental setup for investigating doublestranded telomeric DNA The DNA molecule is chemically bound to a gold surface (via thiolgold chemistry) and picked up by an AFM tip through the streptavidinbiotin interactions (B) Typical forceextension curve of telomeric dsDNA in 100 mM KCl, at pH 47
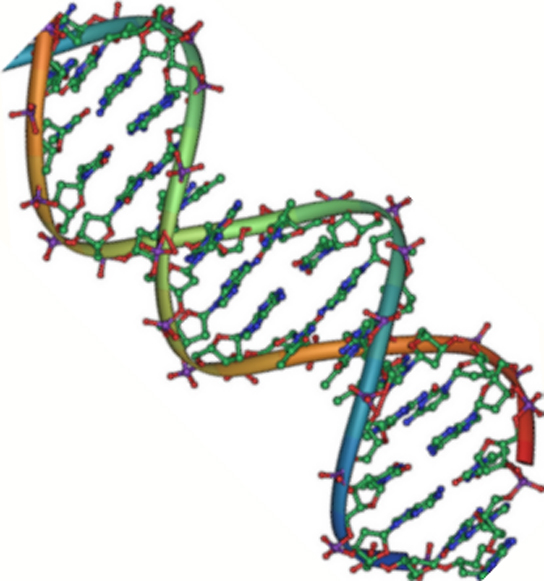


Nucleic Acids Biology For Majors I



How To Draw The Dna Helix Youtube
Nov 12, 18 · Researchers have developed a synthetic molecule that can recognize and bind to doublestranded DNA or RNA under normal physiological conditions The molecule could provide a new platform forThe sugar component of DNA nucleotides double helix the molecular shape of DNA in which two strands of nucleotides wind around each other in a spiral shape nitrogenous base a nitrogencontaining molecule that acts as a base;Aug 05, 17 · In this way, each strand of the original DNA molecule is used to produce a duplicate of its former partner (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)) Whatever information was encoded in the original DNA double helix is now contained in each replicate helix
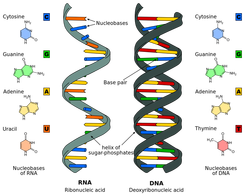


Topic 2 6 Structure Of Dna And Rna Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green



Structure Of Dna Function Summary Diagram Model
Jun 22, 05 · In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by doublestranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, and is a fundamental component in determining its tertiary structure The term entered popular culture with the publication in 1968 of The Double Helix A Personal Account of the Discovery of the Structure of DNA by James Watson The DNA doubleThe antiparallel nature of the doublestranded DNA molecule affects the replication process The DNA POLYMERASES involved in replication can only add NUCLEOTIDES to the 3' OH group of a polynucleotide chain, that is, a DNA strand can only be synthesized in the 5' 3' direction requiring a template running 3' " 5'Sep 28, 17 · $\begingroup$ "doublestranded DNA molecule is comprised of two helical shaped polynucleotides, and are connected together via hydrogen bonding" This is wrong Polynucleotide can be a polyribonucleotide or a polydeoxyribonucleotide and DNA is the latter This definition also asserts that there are helical and nonhelical PN and only the
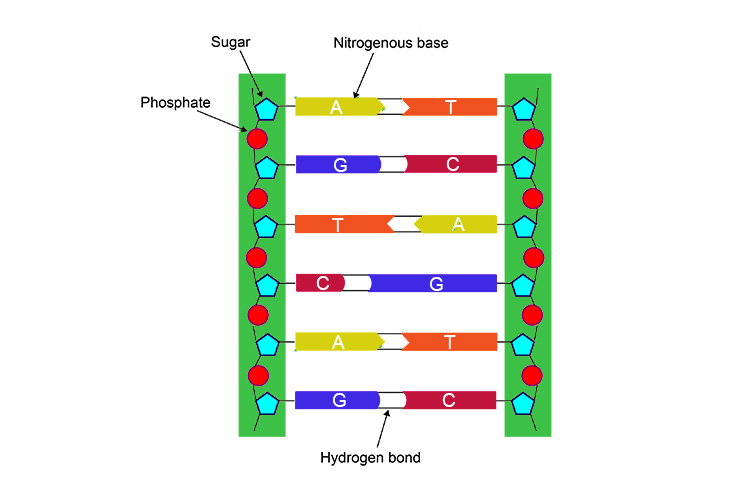


Detailed Page Of The Structure Of Dna And Its Double Helix
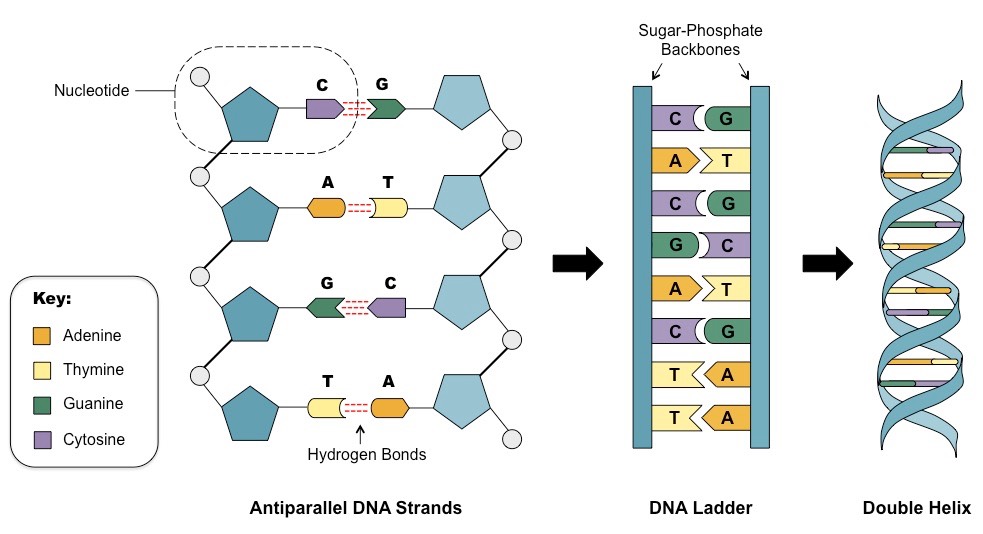


Dna Mechanisms For Storing And Processing Information Part I Sudo Null It News
Viruses may have ~ DNA, ~ RNA, singlestranded DNA or singlestranded RNA The type of genetic material found in a particular virus depends on the nature and function of the specific virus The genetic material is not typically exposed but covered by a protein coat known as a capsid Duplex DNA A ~ DNA molecule DuplicationThe WatsonCrick model of DNA structure postulated that two righthanded polydeoxyribonucleotide chains or strands are coiled in helical fashion around the same axis, thus forming a double helixThe DNA molecule actually consists of two such chains that spiral around an imaginary axis to form a double helix (spiral) Nucleic acid molecules are incredibly complex, containing the code that guarantees the accurate ordering of the amino acids in all proteins made by living cells


Molecular Structure Of Dna Video Khan Academy



Why Is Dna Called A Double Helix Quora
4 What are the 4 bases that make up a DNA molecule?Mar 26, 21 · The flat ligands assemble themselves into coplanar stacks, just like natural bases This results in a double strand made of DNA and palladiumJan 18, 11 · RecA is a key protein in homologous recombination During recombination, one singlestranded DNA (ssDNA) bound to site I in RecA exchanges Watson–Crick pairing with a sequencematched ssDNA that was part of a doublestranded DNA molecule (dsDNA) bound to site II in RecA After strand exchange, heteroduplex dsDNA is bound to site I



Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks



Deoxyribose An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Double Stranded Dna Detailed Structure Download Scientific Diagram
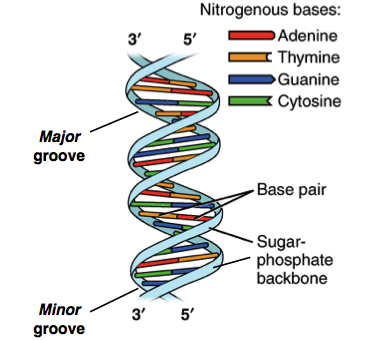


Discovery Of The Structure Of Dna Article Khan Academy
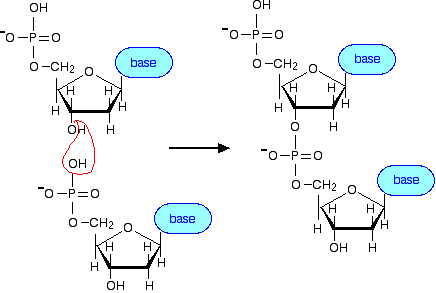


Dna Structure


Dna Structure Contexo Info


Why Do We Write A Dash Beside 5 In A Dna Molecule Quora


Introduction To Dna



Dna Liquid Crystalline Dispersions And Nanoconstructions 1st Edition



Nucleic Acid Definition Function Structure Types Britannica


3 3 Dna Structure Bioninja
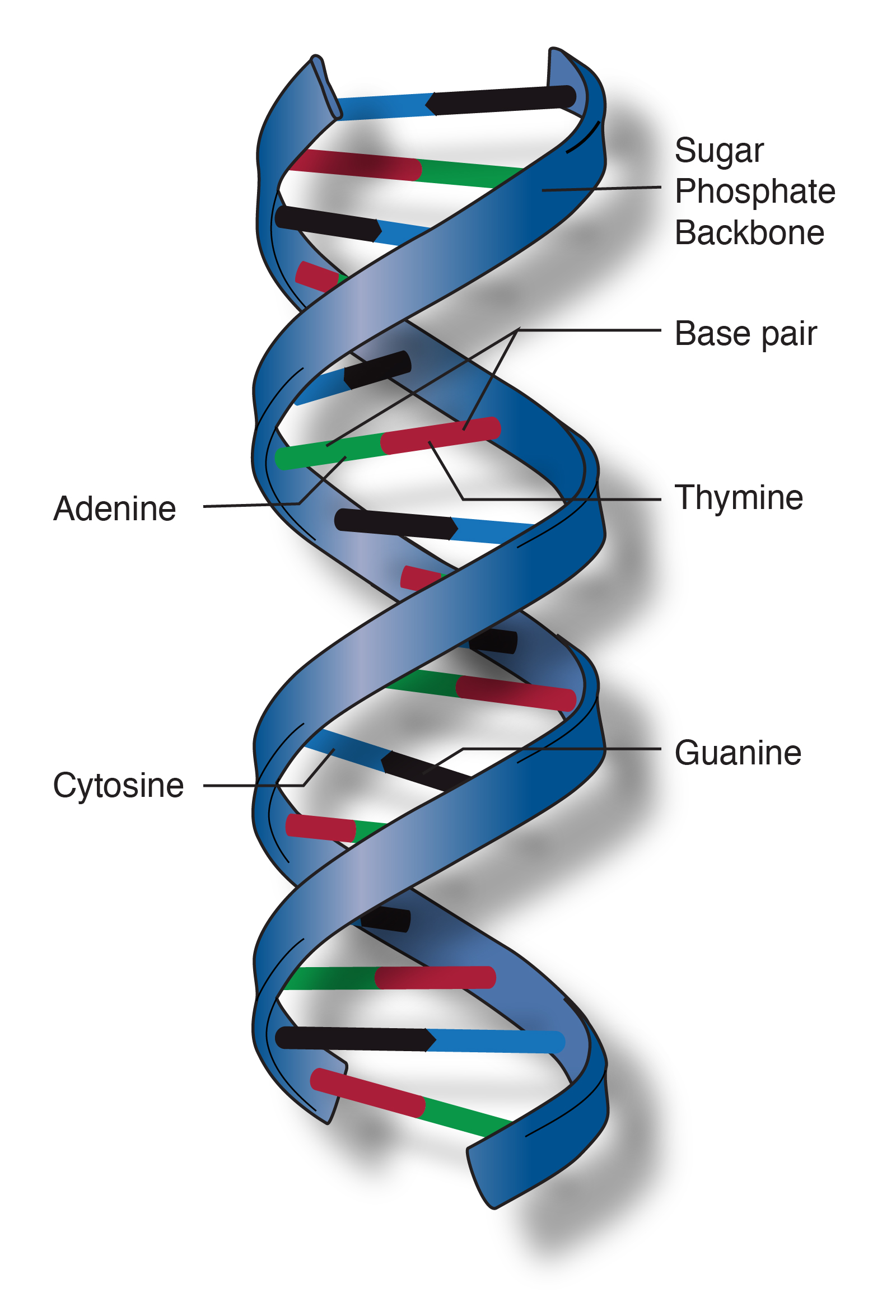


Dna Double Helix



Dna Function Structure With Diagram Article Khan Academy



Diagrams Of Molecular Structure Amine Bases Hydrogen Bonding Base Pairing In Dna And Rna Thymine Adenine Cytosine Guanine Uracil Hydrogen Bonds Hold Hexix Together Double Strabded Rna Dna Organic Nitrogen Compounds Organonitrogen



Dna Replication Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia



Dna Function Structure With Diagram Article Khan Academy
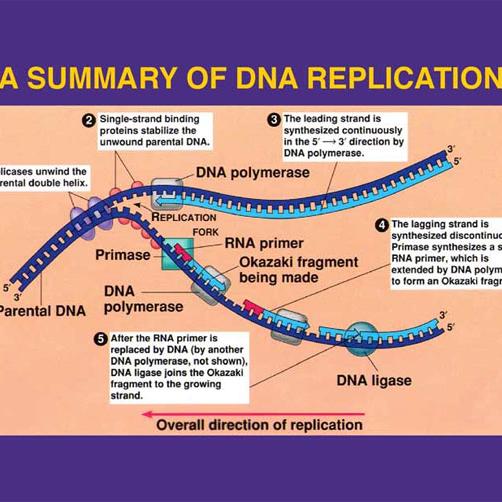


Transcription



2 6 And 2 7 Paper 2 Questions Flashcards Quizlet



What Is The Genome Made Of View As Single Page



1 Schematic Representation Of Double Stranded Dna The Double Helix Download Scientific Diagram


33 Draw And Label A Dna Molecule Labels Database



Discovery Of Dna Double Helix Watson And Crick Learn Science At Scitable



Structural Biochemistry Nucleic Acid Dna Dna Structure Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World



What Is The Genome Made Of View As Single Page



What Makes Up The Backbone Of Dna Science Lesson Project
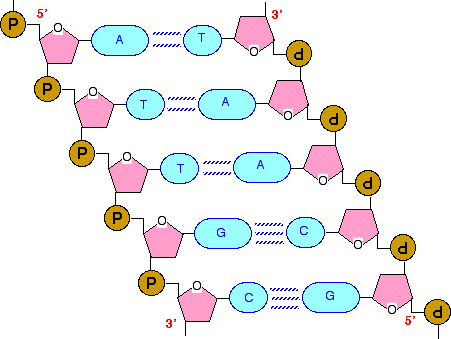


Dna Structure



Structure And Function Of Dna Microbiology



Topic 7 Nucleic Acids And Proteins Ppt Video Online Download
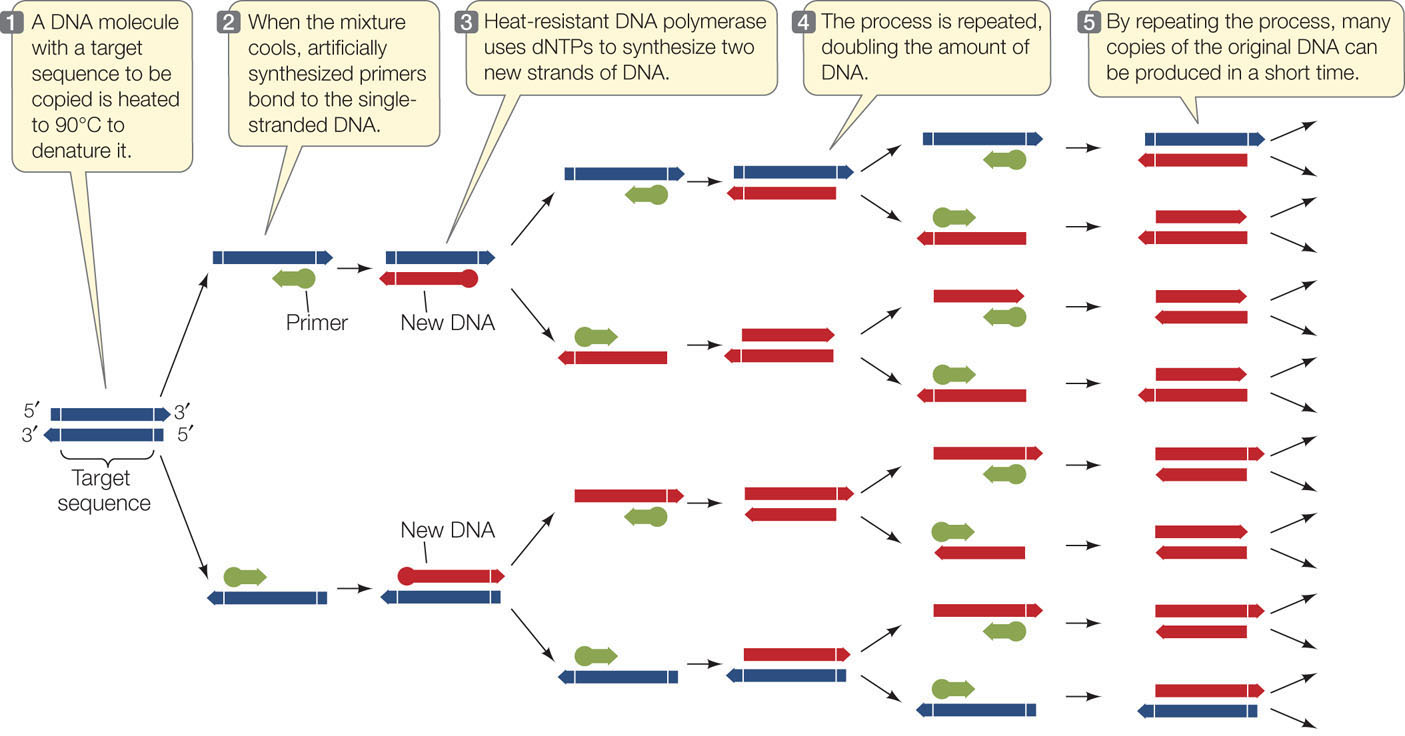


Hillis2e Ch09



2 6 And 2 7 Paper 2 Questions Flashcards Quizlet


The Abc Of Genomics Advanced Nutrigenomics Llc



Genetics Dna Replication Angelicscalliwags
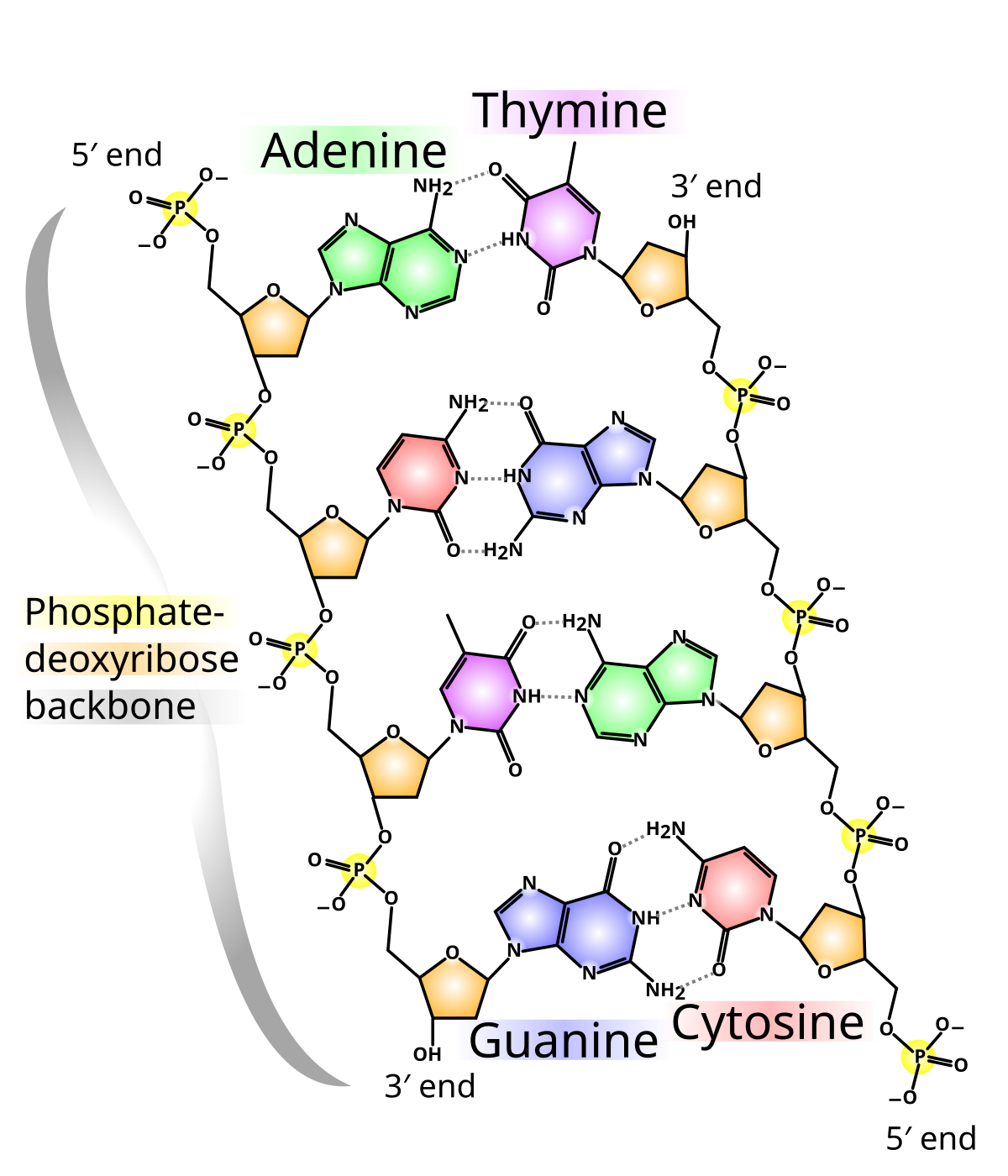


Dna Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia



Dna Definition Function Structure And Discovery Biology Dictionary



3 3 7 1 Dna Structure Hl Caitlin Word Dna Gene



Solved The Unwinding Of A Double Stranded Dna Molecule Is Chegg Com



Dna Explained Structure And Function


9 1 The Structure Of Dna Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition


Amazon Com Dna Model Kit A Industrial Scientific
/dna-versus-rna-608191_sketch_Final-54acdd8f8af04c73817e8811c32905fa.png)


The Differences Between Dna And Rna



Advanced Characterization Of Dna Molecules In Raav Vector Preparations By Single Stranded Virus Next Generation Sequencing Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids



What Is Dna Facts Yourgenome Org



3 3 5 Draw A Simple Diagram Of Dna Structure Youtube
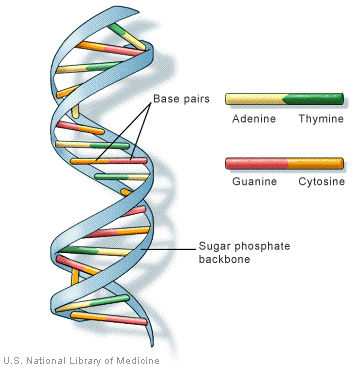


Dna Structure
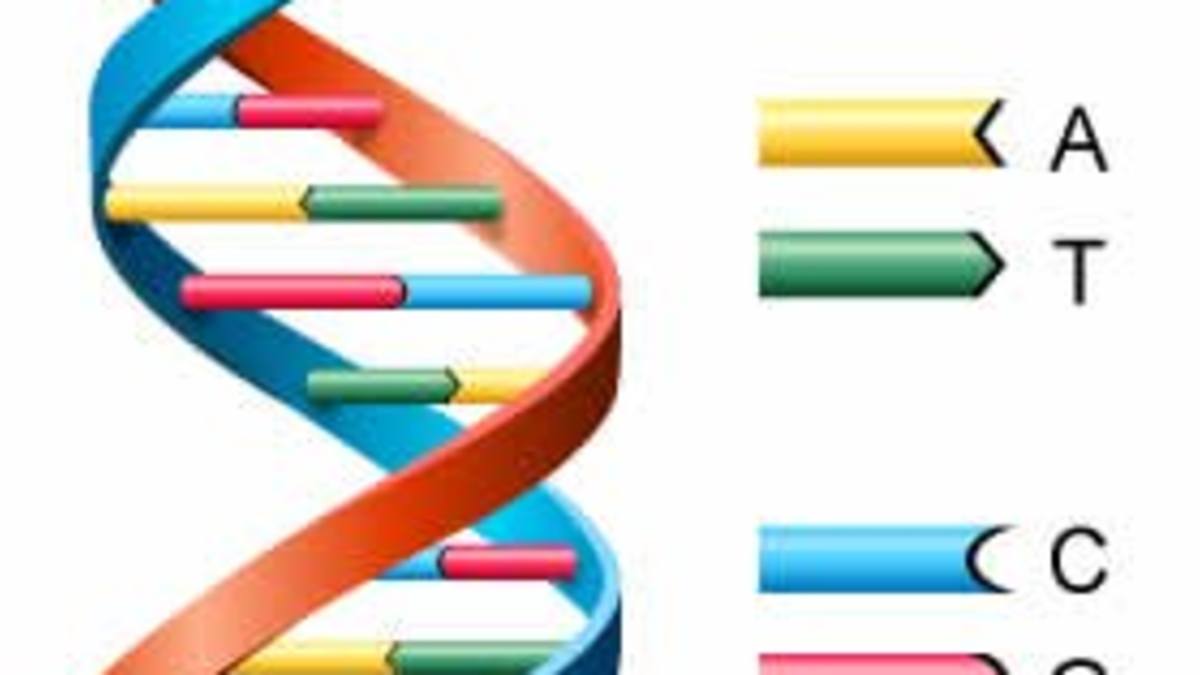



How To Explain Dna To Kids Owlcation



Detailed Page Of The Structure Of Dna And Its Double Helix



Storing Genetic Information Biology For Non Majors I



Discovery Of Dna Double Helix Watson And Crick Learn Science At Scitable



Discovery Of Dna Double Helix Watson And Crick Learn Science At Scitable



Single Stranded Dna Vs Double Stranded Dna Quick Differences In 5 Min Youtube


Symmetry Free Full Text Synchronized Oscillations In Double Helix B Dna Molecules With Mirror Symmetric Codons Html


Dna Replication Definition Enzymes Steps Mechanism Diagram


22 7 Dna Replication The Double Helix And Protein Synthesis Chemistry Libretexts


Structure Of Dna And Rna



Structure Of Dna 1 Primary Structure 2 Secondary Structure 3 Ppt Download



Bioknowledgy 7 1 Dna Structure And Replication Ahl


Dna Model


The Structure Of Dna
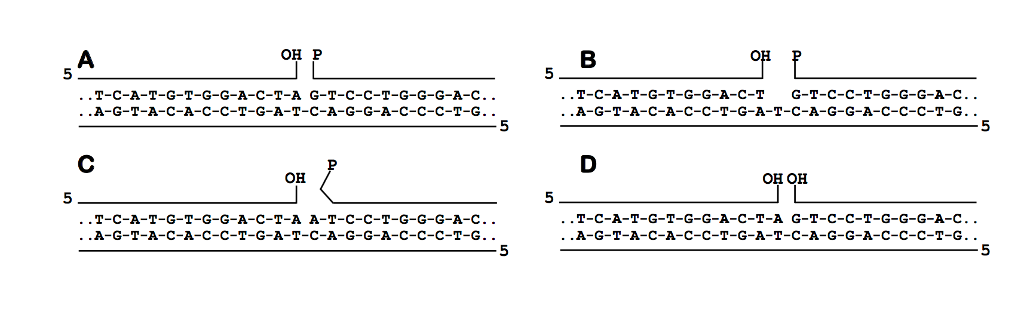


Solved Below Are Diagrams Of Double Stranded Dna Molecule Chegg Com


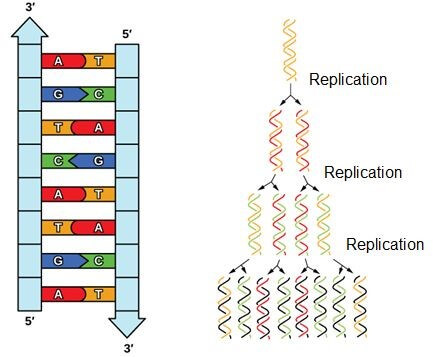
Dna Replication Structure Stages Of Replication Teachmephyiology



The Structure Of Dna


Dna Structure Function A Simple Guide For Beginners
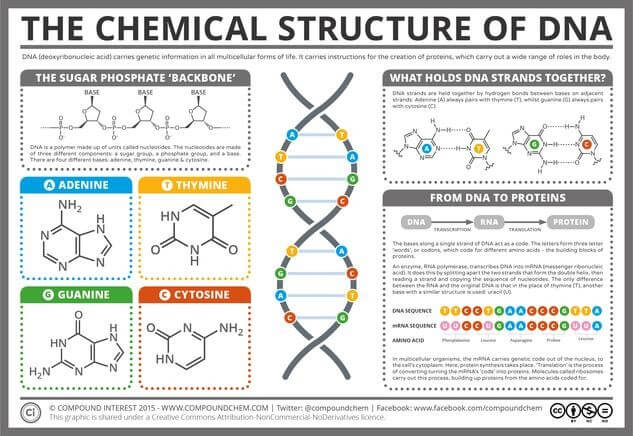


Dna Structure Function A Simple Guide For Beginners



What Is Dna Replication Facts Yourgenome Org



The Structure Of A Double Stranded Dna Dsdna Molecule Download Scientific Diagram



Structure And Function Of Dna Microbiology



Chem435 Physical Chemistry Laboratory Lab 4 Thermodynamics Of Dna
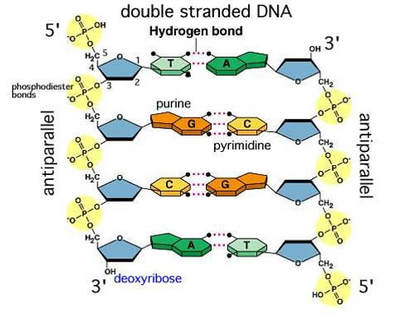


2 6 Dna Rna Structure


Structure Of Nucleic Acids



What Is The Function Of Dna What Does Dna Do Ancestrydna Learning Hub
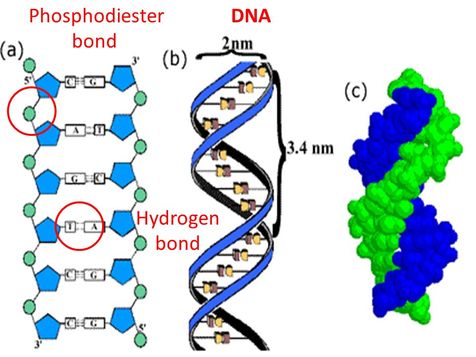


2 6 Dna Rna Structure
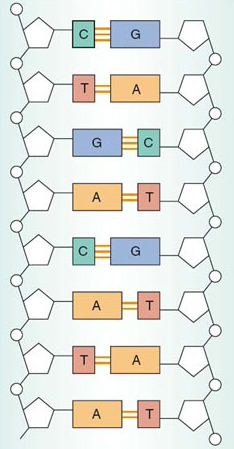


What Is The Genome Made Of View As Single Page
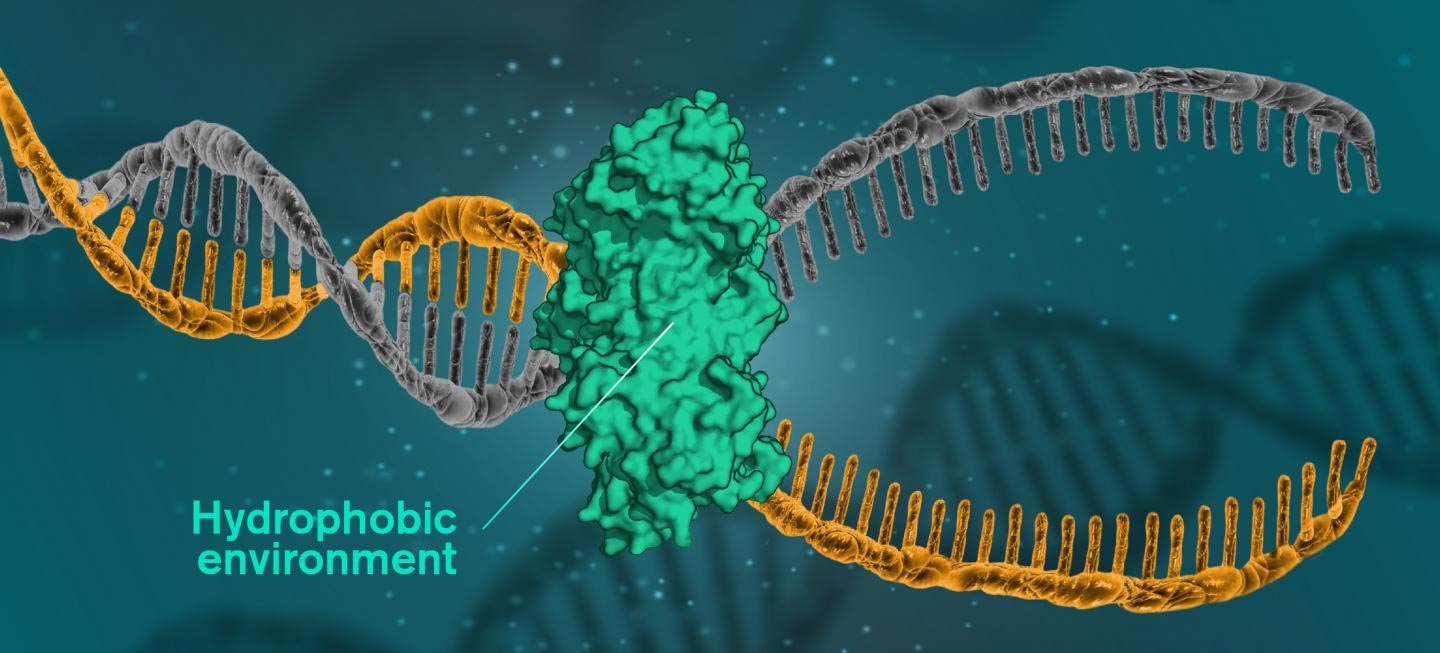


A New Insight Into How Dna Is Held Together By Hydrophobic Effects


9 1 The Structure Of Dna Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition


What Do The Designations 3 5 And 5 3 Refer In A Double Stranded Dna Molecule Quora



Dna Structure Overview Diagrams Expii



Schematic Representation Of A Double Stranded Dna Molecule Of The Zzo Download Scientific Diagram



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿